Military Circuit Procedures
10.15 Military Initial and Pitch Circuit Procedures
10.15.1 For Military fast jet and training aircraft the preferred method ofjoining the circuit is via a procedure known as Initial and Pitch. The aircraft (or formation) will track to the Initial Point, a point at 5NM downwind of the runway in use displaced to the dead side, and track inbound at high speeds (see diagram below - not to scale).
10.15.2 Traffic permitting, Initial and Pitch procedures may be conducted at military, joint user, controlled and non controlled aerodromes. At controlled aerodromes military pilots must comply with ATC circuit entry instructions unless approved for an Initial and Pitchentry.
10.15.3 When conducting this procedure, the height for fast jets is normally 1,500FT AGL and 1,000FT AGL for other aircraft. Aircraft on tactical missions can conduct the initial and pitch at below normal altitudes; this is referred to as a low Initial and Pitch.
10.15.4 At any stage once abeam the threshold of the runway in use, and safe to do so, the aircraft turns ("Pitches") to join downwind and configures for landing.
10.15.5 Generally pilots conducting this manoeuvre will broadcast their position at the Initial Point and on the base turn.
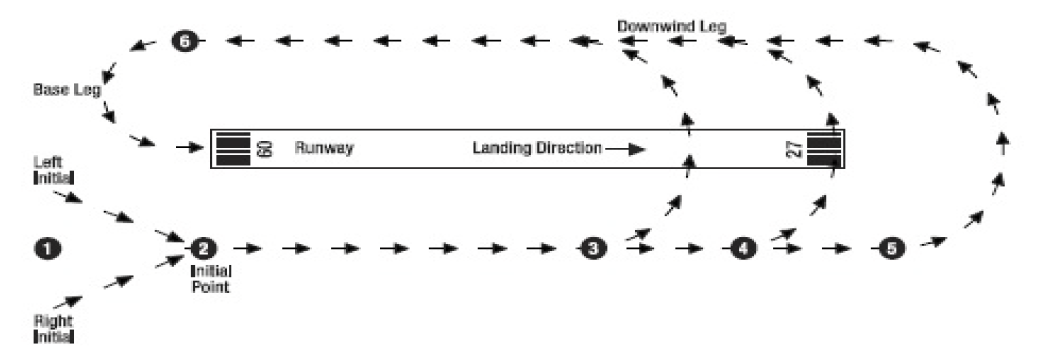
| 1. First call on run-in to Initial Point | 4. Second aircraft in formation pitches out and positions Downwind behind first aircraft. |
| 2. Commence Initial | 5. Subsequent aircraft in formation pitch out and position Downwind behind second aircraft. |
| 3. First aircraft in formation pitches out and positions Downwind | 6. First aircraft calls turning on Base leg for the entire formation. Clearances or instructions apply to the entire formation. Subsequent aircraft in formation will make independent base calls. |
